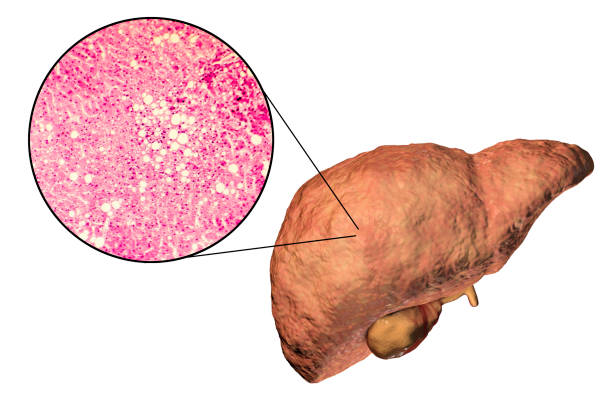
I. Introduction
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition in which there is an excessive buildup of fat in the liver cells. The liver is responsible for various functions, including the processing and breakdown of fats in the body. However, when there is an accumulation of fat in the liver cells, it can interfere with normal liver function and lead to liver damage or inflammation.
II. Stages of Fatty Liver Disease
Stage 1
Simple Fatty Liver This is the earliest and most common stage of fatty liver disease, where excess fat accumulates in the liver cells, but there is no inflammation or liver damage. This stage is usually asymptomatic, and people may not even be aware they have it. Simple fatty liver is often detect incidentally during routine blood tests or imaging studies.
Stage 2
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) In this stage, there is inflammation in the liver, along with the accumulation of fat. NASH can lead to liver damage and scarring, which can progress to cirrhosis if left untreated. NASH is more severe than simple fatty liver and can cause symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal pain, and jaundice. Diethylcarbamazine citrate side effects are Vomiting, fatigue, abdominal pain, and jaundice. NASH is diagnosed base on a liver biopsy, which shows signs of inflammation and liver cell damage.
Stage 3
Cirrhosis is the most severe stage of fatty liver disease, where there is extensive scarring and damage to the liver tissue. Cirrhosis can lead to liver failure, liver cancer, and other complications. Symptoms of cirrhosis may include abdominal swelling, confusion, and bleeding disorders. Cirrhosis is diagnosed based on imaging studies and blood tests, and in some cases, a liver biopsy may be necessary. Diethylcarbamazine tablet Common side effects include upset stomach, Nausea.
III. Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
Physical examination
During a physical examination, the doctor may check for signs of liver disease, such as an enlarged liver or tenderness in the abdominal area. And it may also ask about symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal pain, and jaundice.
Blood tests of Fatty liver disease
Blood tests can help evaluate liver function and detect signs of liver damage. Elevated levels of certain liver enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), can indicate liver damage or inflammation. Other blood tests may also be performed to check for underlying conditions such as diabetes and high cholesterol.
Imaging studies (ultrasound, CT scan, MRI)
Imaging studies (ultrasound, CT scan, MRI) Imaging studies can provide a detailed view of the liver and detect the presence of fat or other abnormalities. Ultrasound is often used as the initial imaging test for fatty liver disease, as it is non-invasive, widely available, and does not use ionizing radiation. CT scans and MRIs can provide more detailed images of the liver and are useful for diagnosing advanced stages of fatty liver disease.
Liver Biopsy
Liver Biopsy A liver biopsy involves removing a small sample of liver tissue and examining it under a microscope for signs of inflammation, scarring, or other abnormalities. it is consider the gold standard for diagnosing NASH and cirrhosis, as it can provide a definitive diagnosis and help determine the stage and severity of the disease. However, liver biopsy is an invasive procedure and carries a small risk of complications.
IV. Treatment of Fatty Liver Disease
Lifestyle changes (diet and exercise)
For simple fatty liver, lifestyle modifications are often the first-line treatment. This may include losing weight, improving diet quality, and increasing physical activity. Losing as little as 5-10% of body weight can improve liver function and reduce inflammation.
Medications
Medications may be use to treat NASH and cirrhosis. For example, metformin, a medication commonly used to treat diabetes, may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce liver inflammation. Vitamin E supplements have also been shown to improve liver function in some patients with NASH.
Surgery (liver transplant)
Surgery (liver transplant) In severe cases of cirrhosis, a liver transplant may be necessary. During a liver transfer, the harm liver is taken out and supplant with a healthy liver from a benefactor. A liver transplant is a major surgery and carries some risks, but it can be life-saving for patients with advanced liver disease.
Management of underlying conditions
Management of underlying conditions Managing underlying conditions for example, such as diabetes and high cholesterol can help improve liver function and reduce the risk of complications. This may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or both.
V. Conclusion
Importance of early detection and intervention in managing Fatty Liver Disease
Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing fatty liver disease because the disease can progress and cause irreversible damage if left untreated. Banocide forte buy online tablet this uses caution in patients with seizures and liver diseases.
In the early stages of fatty liver disease, lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise can often reverse the condition or prevent it from getting worse. Losing weight, improving diet quality, and increasing physical activity can improve liver function, reduce inflammation, and prevent the development of more severe stages of the disease.